Last update
2023
Summary
This project combined several natural water retention measures: restoration of meadows and pastures, reduced tillage, reduced stocking density, and wetland restoration . Located in north-west Germany (Weser basin, DE4000), it was funded under the LIFE Program and aligned with the WFD, Habitats, and Birds Directives. Since 2017, over 30 ha of wetlands have been restored, and a reed polder (>80 ha) is being developed to reduce phosphorus loads. Additional river restoration measures have been implemented in the Hunte and Elze catchments. The project involved a wide range of stakeholders, including conservation bodies, water managers, farmers, and local NGOs. It successfully increased meadow bird populations and fostered constructive stakeholder cooperation. Recent efforts also include fish removal and a shift from technical to nature-based solutions, with key goals targeted for 2027.
Position
Latitude
52.5106507
Longitude
8.3411022
Project
NWRM
National Id
Germany_03
Installation date
2007-12
Implementation Status
Contact
Tamer Fawzy / BEF DE
RBD code
DE4000
Transboundary
0
Photo gallery
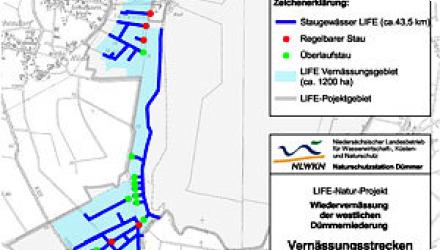
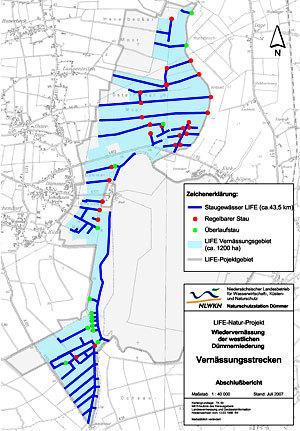
Location of the project
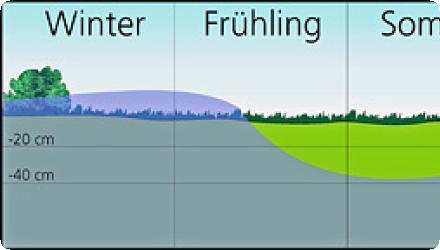
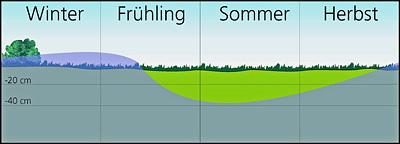
The Dümmer lowland in the northwest German plain consists of extensive marshes and wet grassland that are flooded in winter.
NUTS Code
DE92 - Hannover
Involved Partners
| Authority type | Authority name | Role | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Climate zone
cool temperate moist
Temperature
9
Annual rainfall range
600 - 900 mm
Runoff range
150 - 300 mm
Slope range
nearly level (0-1%)
Water quality status
Although it can be assumed that the measure had reduced nutrients in the groundwater of the area, no quantitative assessments were carried out prior to the implementation.
Performance timescale
Immediate
Project area
2500
Area specifications
Usability, integrative planning, acceptability
Area subject to Land use change or Management/Practice change (ha)
2500
Lifespan
40
The wetlands of the Dümmer lowland area are of international significance for nature conservation. The diverse natural and nearnatural habitats hold a large number of bird species (reed, wading, water and meadow birds), which breed, rest or winter here.
Various developments have greatly endangered these bird's paradise in the past. The diking of the Dümmer lake in 1953 has led to the drainage of the wetlands and the intensification of agricultural activity.
Together with the cutting of peat in the adjacent bogs, this has caused the water to be heavily polluted with nutrients.
Various developments have greatly endangered these bird's paradise in the past. The diking of the Dümmer lake in 1953 has led to the drainage of the wetlands and the intensification of agricultural activity.
Together with the cutting of peat in the adjacent bogs, this has caused the water to be heavily polluted with nutrients.
Before the project, over 2000 ha were already acquired for the Bird Sanctuary of Lake Dümmer. A well established, institutionalized Round Table served as a communication platform between Nature Conservationists and Farmers, so that acceptance was guaranteed throughout the process.
Total cost
€ 3,100,000
Costs investment
2000000
Costs investment information
land acquisition
Costs land acquisition
2000000
Costs land acquisition unit
€ (total value)
Costs operational
800000
Costs operational information
Supporting dams and removal of drainages
Costs operation maintenance
1100000
Costs maintenance
300000
Financing authorities
Type of funding
EU-funds: LIFE+
Compensations
0
Policy context
Wide, open grasslands and meadow birds are a part of the historic cultural landscape of meadows and pastures in Northern Germany. Intensified agriculture in Lower Saxony, as well as in many other places, puts a threat on this landscape and local meadow bird populations. The draining of meadows, early mowing, and densification of the ground through heavy machinery render these areas practically unlivable for meadow birds. Meadow birds breed and raise their chicks on the ground in grassland areas. After hatching, the chicks need about four weeks before they are able to fly. Until then, they collect insects and worms from the vegetation and the ground under attendance of their parents. When they reach maturity, meadow birds use their long beaks to pick for food in the wet soil. Suitable habitats for meadow birds have decreased strongly in size, and the grassland remaining today, does not provide ideal conditions. Consequently, the number of meadow birds declined sharply in recent decades.
Community involvment
No
Design consultation activity
| Activity stage | Name | Key issues | Comments |
|---|
Policy target
| Target purpose |
|---|
|
Improved Biodiversity
|
Target Remarks
Regulation of hydrological cycle and water flow
Habitat restoration
Habitat restoration
Policy pressure
| Pressure directive | Relevant pressure |
|---|---|
|
WFD identified pressure
|
Nutrient pollution
|
|
Floods Directive identified pressure
|
Protected Areas
|
|
Floods Directive identified pressure
|
Landscape
|
Policy impact
| Impact directive | Relevant impact |
|---|
Requirement directive
| Requirement directive | Specification |
|---|
Contractual arrangements
1
| Arrangement type | Responsibility | Role | Name | Comments |
|---|
Part of wider plan
1
Wider plan type
| Wider plan type | Wider plan focus | Name | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Environment & Biodiversity
|
Natura 2000
|
Regularly (weekly to monthly)
Biodiversity/ meadow bird breeding success
Maintenance
After the project could be finished, management of the rewetting areas will continuously be guaranteed by the nature conservation base Dümmer.
Catchment outlet
meadow bird breeding success monitoring
There were no methods used to assess costs and the cost-effectiveness of the measure. The benefit was measured by monitoring the breeding success of meadow birds, though.
Two nature trails were created along the western bank of the lake, which tie up to the few years old nature trail "Dümmer” in Ochsenmoor. The special natural features of the Dümmer lowlands are displayed to cyclists and hikers.
While the short trail around Olgahafen was specially designed for hikers, the trail stations along the further course of the bank are mainly set up for cyclists. Four of these stations have an interactive design.
The youth- and holiday center of Vechta district is situated next to the start of the nature trails. About 10,000 people, mainly pupils with their school classes, visit this center every year. Especially for this clientele as well as for other interested visitors the "nature trail quiz rally” was developed.
Furthermore the restoration of the habitat led to increased tourist numbers.
While the short trail around Olgahafen was specially designed for hikers, the trail stations along the further course of the bank are mainly set up for cyclists. Four of these stations have an interactive design.
The youth- and holiday center of Vechta district is situated next to the start of the nature trails. About 10,000 people, mainly pupils with their school classes, visit this center every year. Especially for this clientele as well as for other interested visitors the "nature trail quiz rally” was developed.
Furthermore the restoration of the habitat led to increased tourist numbers.
Biomass production, tourism, recreation, Water security
Information on retained water
N.A.
Information on increased water storage
N.A.
Information on runoff reduction
N.A.
Water quality overall improvements
N/A info
Soil quality overall soil improvements
N/A info
1
improvements of the meadow bird communities
Ecosystem impact climate regulation
No specific impact
Ecosystem provisioning services
1
Information on Ecosystem provisioning services
extensified grassland maintainence
Key lessons
Lessons learned in this project reach from practical and technical experience to the integration of stakeholders to achieve a high acceptance and participation of local farmers.
The experience from this project also led to the initiation of the LIFE+ Project Meadow Birds, including water retention measures in 12 project areas.
The experience from this project also led to the initiation of the LIFE+ Project Meadow Birds, including water retention measures in 12 project areas.
Success factor(s)
| Success factor type | Success factor role | Comments | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Financing possibilities
|
main factor
|
<p>for land acquisition</p>
|
1
|
|
Attitude of relevant stakeholders
|
secondary factor
|
<p>acceptance of relevant stakeholders</p>
|
2
|
Driver
| Driver type | Driver role | Comments | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Organisation committed to it
|
main driver
|
Bird protection / natura200 site
|
1
|
English