Last update
2013
Summary
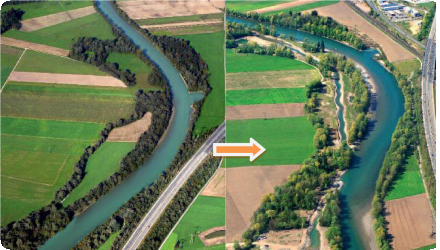
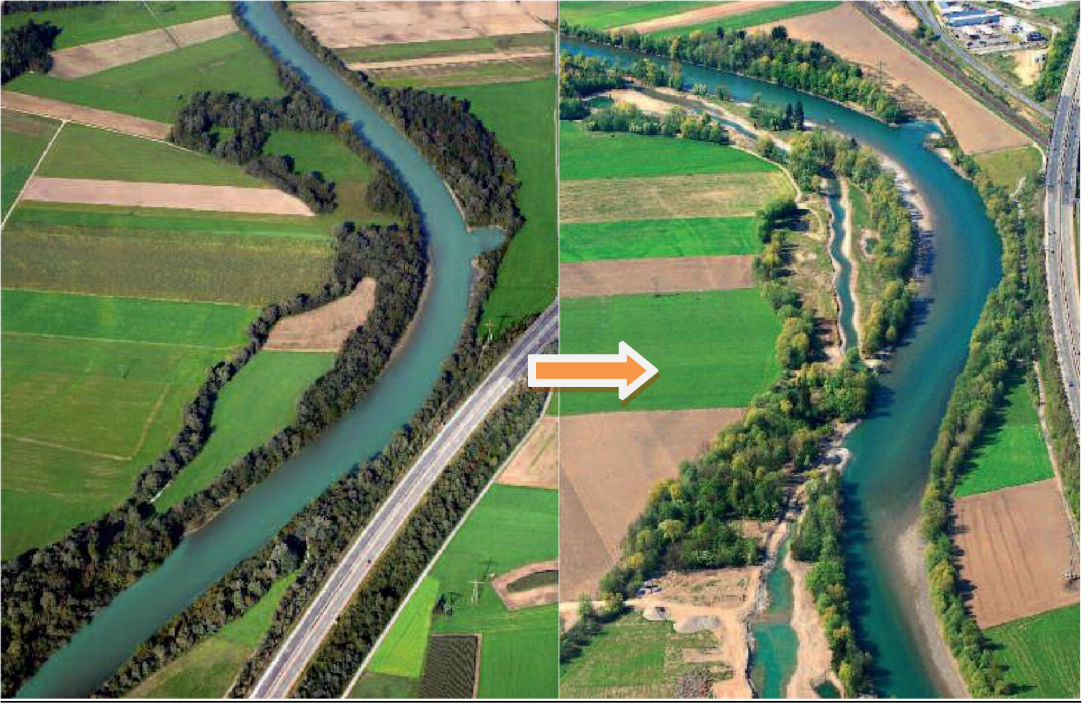
At three different sections of the Austrian Drau the river bed was enlarged and restoration works have taken place. Moreover, 25 ha of riparian forest were created as well as meadows, lakes and several river branches.
Position
Latitude
46.748666
Longitude
12.96743
Project
NWRM
National Id
Austria_01
Installation date
2006-2011
Contact
Sabine Tutte, ACTeon
RBD code
AT1000
Transboundary
1
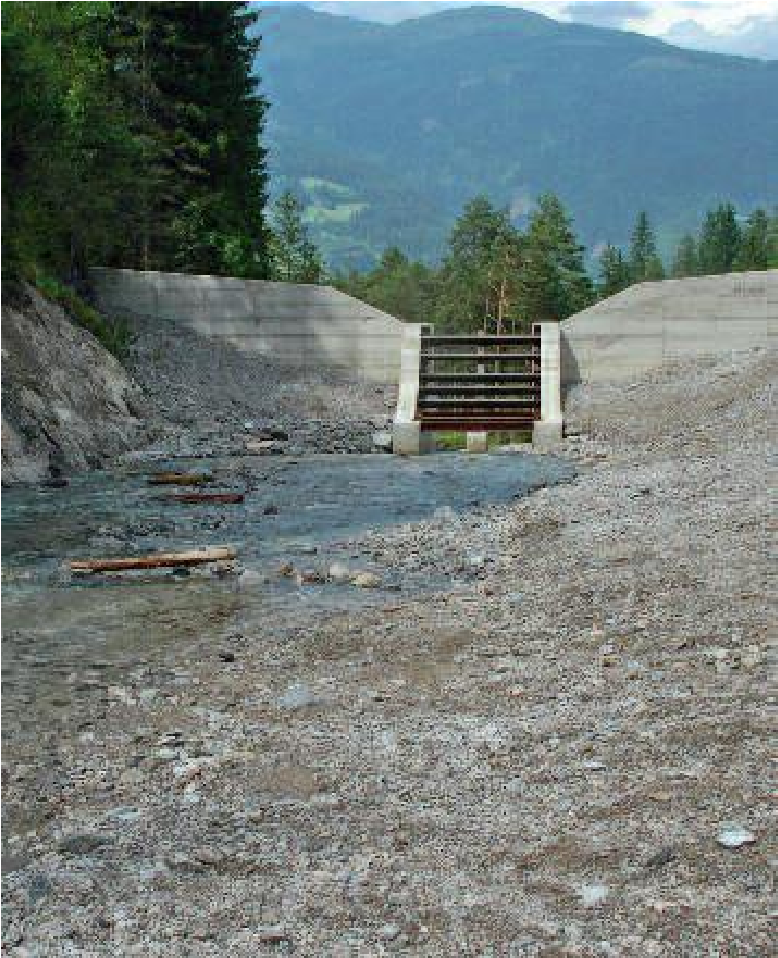
Photo gallery
Location of the project
The project side lies close to the Italian border in the west of Klagenfurt. The revitalized parts of the Drau are between Spittal i.Dr. and Oberdrauburg.
NUTS Code
AT21 - Kärnten
Involved Partners
| Authority type | Authority name | Role | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
Climate zone
cool temperate moist
Temperature
7
Precipitation
1100
Annual rainfall range
1200 - 1500 mm
Runoff
73,8
Runoff range
600 - 750 mm
Elevation range
625
Slope range
0-1%
Vegetation class
In the surroundings of the upper Drau one can find a big variety of different landuses: forest, meadows, fields.
Water bodies: Ecological Status
Poor
Water bodies: Chemical Status
Failing to achieve good
Water quality status
Given that water quality improvement was not an objective of the project, no information is available.
Project scale
Meso
Project scale specification
Although the enlargement of the river bed was done on a length of 5 km the affected length of the river/region around the river is 68 km. The surface of the project region (river and surroundings) are 976 ha.
1 ha meadow lakes, 25 ha riparian forests
1 ha meadow lakes, 25 ha riparian forests
Performance timescale
5 - 10 years
Project area
26
Size
5
Size unit
km
Lifespan
Eternity, exception: the river “decides” to search itself a completely new bed
As already explained the erosion of the river bed (the Drau became deeper and deeper) determined the choice of measures. Another point to mention is the availability of land. Next to the negotiations with farmers a reallocation of land took place. Plots were exchanged between farmers and the project responsible. Depending on the size of riparian buffers available the measurements were adapted.
A good ecological status should be achieved for the Drau river. The measurements combine habitat diversity with passive flood protection. Secondary the regional tourism department supported the project by designing picnic areas, positioning info points and marketing the project.
A good ecological status should be achieved for the Drau river. The measurements combine habitat diversity with passive flood protection. Secondary the regional tourism department supported the project by designing picnic areas, positioning info points and marketing the project.
Design capacity description
Since flood protection wasn’t the main target of the project quantitative data is missing on the success of the implemented NWRM. Monitoring may be done in future. After Norbert Sereinig it is moreover difficult to describe effects on water retention. The flood plains are designed in a way that already quinquennial and decennial floods enter the floodplains completely.
The availability of land determines which measures can be used and how expensive the implementation of the measures will be.
The erosion of the river bed should be stopped. This goal determined the choice of measures.
Total cost
€ 4,475,000
Costs total information
total costs of the project
Costs capital
€ 3,930,000
Costs capital information
Construction, staff, journeys, measuring instruments, gauges
Costs land acquisition
€ 670,000
Costs land acquisition unit
€ (total value)
Costs land acquisition information
Purchase of land
Costs operational
10000 €/yr
Costs operational information
Monitoring of the river bed
Costs operation maintenance information
No special, project-linked expenses.
Every few years maintenance has to be done as on every other river like cutting grass or trees.
Every few years maintenance has to be done as on every other river like cutting grass or trees.
Costs maintenance
0 €
Costs maintenance information
No project-specific maintenance needed
Economic costs other annual
98000
Financing authorities
Type of funding
EU-funds: LIFE+
Comments
1.5 Million €
Type of funding
Sub-national funds
Comments
0.2 Million €
Type of funding
Sub-national funds
Comments
0.2 Million €
Type of funding
National funds
Comments
Forestry, Environment and Water Management 2.7 Mio €
Policy context
The river bed is too narrow and there is a lack of brash and pebbles. As consequence the river bed became deeper, bank stabilization got insecure and flood plains inoperable.
Community involvment
Yes
Design consultation activity
| Activity stage | Name | Key issues | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Implementation phase
|
public inaugauration feasts e.g. for the new dam or the different enlarged riverparts
|
||
|
Implementation phase
|
information day for school children
|
||
|
Implementation phase
|
tree planting event for children
|
||
|
Design phase
|
tourism concept, guided routes within the national park
|
||
|
Other
|
post card showing before after pictures of the drau
|
||
|
Implementation phase
|
VIP event: Mimi Hughes (marathon swimmer and environmental activist swam through the drau until danube
|
Policy target
| Target purpose |
|---|
|
Runoff control
|
|
Improved Biodiversity
|
|
Increase Water Storage
|
Target Remarks
Flood control and flood risk mitigation
Soil formation and maintenance
Biodiversity and gene-pool conservation in riparia
Soil formation and maintenance
Biodiversity and gene-pool conservation in riparia
Policy pressure
| Pressure directive | Relevant pressure |
|---|---|
|
WFD identified pressure
|
Physical alteration of channel/bed/riparian area/shore of water body for agriculture and transportation.
|
Pressures remarks
Bed load balance shall be achieved. Due to missing pebble supply the Drau river bed became deeper and deeper. Thus the groundwater level decreased, bank stabilization became insecure and flood plains inoperable.
Policy impact
| Impact directive | Relevant impact |
|---|---|
|
WFD identified impact
|
Altered habitats due to morphological changes
|
|
WFD identified impact
|
Damage to groundwater dependent terrestrial ecosystems for chemical / quantitative reasons
|
|
Floods Directive identified impact
|
Property
|
|
Floods Directive identified impact
|
Infrastructure
|
Requirement directive
| Requirement directive | Specification |
|---|
Requirement directive remarks
A good ecological status of the Drau should be achieved in order to meet the demands of the WFD.
Policy challenges requirements
The project follows a master plan for the development of the river. With RIWA-T technical guidelines are established that give priority to passive flood protection and take into account the ecological functions of a water body .
Contractual arrangements
0
| Arrangement type | Responsibility | Role | Name | Comments |
|---|
Part of wider plan
1
Wider plan type
| Wider plan type | Wider plan focus | Name | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Catchment-based
|
Water
|
water body-development-concept
|
Plan made in the middle of 90s (93 or 94). Programme for the whole river Drau.
|
The monitoring is still ongoing for the riverbed. It is controlled whether bedload balance is reached and whether the erosion of the bed is stopped. Given that the Drau is let more freedom to form its river bed monitoring is done how the shape of the river develops. The biological monitoring is accomplished. The number of fisch, amphibian and insect species were counted
Maintenance
There are no project-specific maintenance requirements. As for every river every few years grass will be needed to cut as well as trees.
Catchment outlet
-Assessment of aerial photos
- Geodetic survey of cross profiles (echolot)
- Laserscanning with drones
- Steel plates are on the bottom of the river in order to measure the transported load in size and volume with ultrasound
- Life space mapping
- Geodetic survey of cross profiles (echolot)
- Laserscanning with drones
- Steel plates are on the bottom of the river in order to measure the transported load in size and volume with ultrasound
- Life space mapping
3250000
Total expenses for the implementation of the project given to regional companies, planning offices.
The tourism department definitetly benefitted from the Drau project but this cannot be quantified yet.
Hydrological effects
Until mid 2011 28000 km3 were mobilized by the open checked dam and 16000 km3 arrived at the Drau. As consequence the bedload balance could be improved and the riverbed stabilized.
Information on retained water
No quantitative data. However riparian forests were planted and buffer stripes installed along the river shore. These measurements favour an increase of water storage capacity.
Information on increased water storage
No quantitative data. Side arms were reconnected to the main channel and the riverbed itself was enlarged. As a consequence storage capacity must have increased.
Information on runoff reduction
no data available
Water quality overall improvements
N/A info
Information on Water quality overall improvements
Riparian forests may act as buffers for diffuse pollution input for water from fields (nitrogen, phosphorous, herbicide flux).
Soil quality overall soil improvements
N/A info
Information on Soil quality overall soil improvements
No monitoring is done on this aspect since it was not targeted in the project.
1
Number of amphibian species multiplied by six.
Number of insect and fish species increased as well, new habitats and higher habitat quality for fish and their breeding, more than 100 spider and ground beetle species several of which are endangered or threatened by extinction .
Number of insect and fish species increased as well, new habitats and higher habitat quality for fish and their breeding, more than 100 spider and ground beetle species several of which are endangered or threatened by extinction .
Ecosystem impact climate regulation
Increased permanent biomas
Information on Ecosystem impact climate regulation
Given that buffer strips, riparian forests and meadows were created/restored permanent biomas has increased.
Ecosystem provisioning services
0
Information on Ecosystem provisioning services
no information available
Key lessons
By adapting open check dams the bed load balance of a river can be improved. The reconnections of side arms, the creation of riparian forests and meadows support a greater biodiversity.
The adaptation of open check dams to improve bed load balance is possible. The widening of the river bed and the reconnection of side arms create larger habitat diversity and as consequence the number of species in the area rises.
The adaptation of open check dams to improve bed load balance is possible. The widening of the river bed and the reconnection of side arms create larger habitat diversity and as consequence the number of species in the area rises.
Success factor(s)
| Success factor type | Success factor role | Comments | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Attitude of the public
|
main factor
|
<p>Since the revitalization measures on the Drau are a subsequent project to former projects and measures, much less publicity had to be done. The responsibles hadn't to face the fears and worries of farmers and citizens.</p>
|
1
|
|
Existing staff and consultant knowledge
|
main factor
|
<p>20 years of experience exist on restoring the river to a more natural state. Moreover, there is good cooperation between the different stakeholders for nature conservation and hydraulic engineering.</p>
|
2
|
|
Other
|
secondary factor
|
<p>The regional touristic department supported the measure and furthermore helped to merchandise the Drau project. They looked amongst others at the following questions: How to design picnic areas? Where are the best places for information boards? How can we conduct tourists through the region?</p>
|
3
|
|
Attitude of decision makers
|
main factor
|
<p>The purchase of land was combined with a reallocation of land process. Lots were exchanged between farmers. There were a lot of farmers willing to give land for the project and there was also political support of the action. A company constructing/operating hydropower plants had bought lots in the 90s. After their project of building 4 new power plants on the Drau was refused they were nevertheless ready to give their lots to the project partners for a fair price.</p>
|
4
|
Driver
| Driver type | Driver role | Comments | Order |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Other
|
main driver
|
Erosion of the river bed was observed (becoming deeper and deeper). There was furthermore a risk that floodplains fall dry and can't operate anymore, as well as a risk of a falling ground water table.
|
1
|
Flexibility adaptability
Since the river has freedom to form its bed, it will adapt the measures on its own. The adaptation of the measures by humans is linked with huge costs and difficult to execute.
Transferability
There has to be knowledge about the original characteristics of the river. Was it a branched or meandering river?
English